Sebaceous Glands and Hair – Sebaceous glands are small, oil-producing glands found throughout the skin. They are typically attached to hair follicles and are responsible for producing sebum, an oily substance that lubricates the skin and hair. In this article, we will delve into the anatomy and function of sebaceous glands, their relationship with hair, common disorders associated with them, and tips for maintaining their health.
Introduction
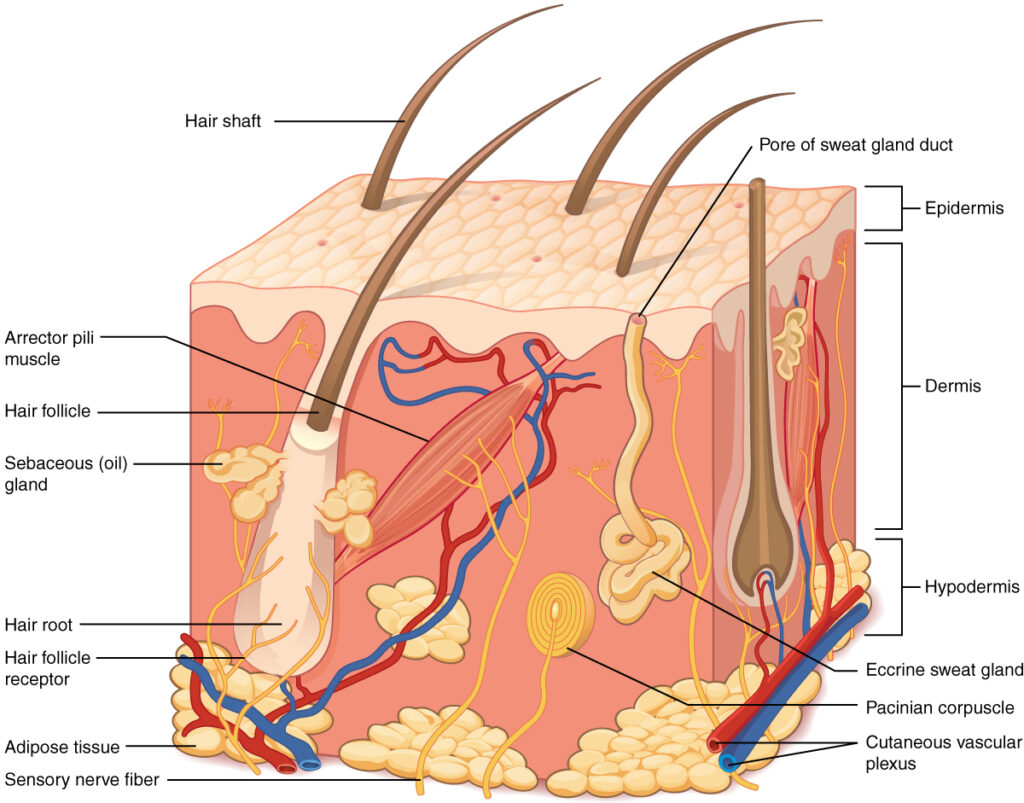
Sebaceous glands are integral components of the skin’s structure, primarily located in the dermis. Their main function is to produce sebum, a mixture of lipids, wax esters, and cellular debris. Sebum plays a crucial role in skin hydration and protection against environmental factors.
Anatomy of Sebaceous Glands
Sebaceous glands are distributed across the skin, with higher concentrations on the face and scalp. They are connected to hair follicles and consist of sebocytes, specialized cells that synthesize and store sebum. These glands vary in size and shape, with larger glands typically found on the face and smaller ones on the body.
Production of Sebum
Sebum production begins within sebocytes, where lipids are synthesized and stored in lipid droplets. As the sebocytes mature, they release sebum into the hair follicle through a process called holocrine secretion. This process is regulated by hormones, such as androgens, and can be influenced by factors like genetics, age, and environmental conditions.
Importance of Sebum
Sebum plays a crucial role in maintaining skin health. It helps lubricate the skin, keeping it soft and supple, while also forming a protective barrier against microbial invasion and dehydration. Additionally, sebum contains antioxidants that neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and preventing premature aging.
Sebum and Hair
Sebum also plays a vital role in hair health. It coats the hair shaft, providing lubrication and protection against damage. Sebum acts as a natural conditioner, keeping the hair hydrated and preventing it from becoming dry and brittle. However, excessive sebum production can lead to oily scalp and hair, which may contribute to conditions like dandruff and acne.
Common Disorders of Sebaceous Glands
Several disorders can affect the function of sebaceous glands, leading to various skin conditions. Acne is one of the most common disorders, characterized by the overproduction of sebum, clogging of hair follicles, and inflammation. Seborrheic dermatitis is another common condition, characterized by red, itchy, and flaky skin, often occurring on the scalp, face, and chest. Sebaceous hyperplasia, a benign enlargement of sebaceous glands, can also occur, resulting in raised bumps on the skin.
Tips for Healthy Sebaceous Glands and Hair
Maintaining healthy sebaceous glands and hair requires proper skincare and lifestyle habits. This includes:
- Proper hygiene: Regular cleansing helps remove excess sebum, dirt, and impurities from the skin and hair.
- Balanced diet: Consuming a diet rich in essential nutrients, such as vitamins A, C, and E, promotes skin and hair health.
- Avoiding harsh products: Using gentle skincare and haircare products minimizes irritation and helps maintain the natural balance of sebum production.
Conclusion
Sebaceous glands play a crucial role in maintaining skin and hair health. Understanding their anatomy, function, and relationship with hair can help individuals make informed decisions about skincare and haircare practices. By adopting healthy habits and addressing any underlying disorders, individuals can support the optimal function of sebaceous glands and promote overall skin and hair wellness.
FAQs
- What causes overactive sebaceous glands?
- Overactive sebaceous glands can be caused by hormonal imbalances, genetics, stress, and certain medications.
- Can sebum production be controlled?
- While sebum production is primarily regulated by hormones, certain skincare products and lifestyle changes can help manage excess oiliness.
- Is sebum good for the skin?
- Yes, sebum is essential for maintaining skin hydration and protection. However, excess sebum can contribute to skin problems like acne.
- How can I reduce oily skin?
- Maintaining a consistent skincare routine, avoiding harsh products, and managing stress levels can help reduce excess oiliness.
- Can seborrheic dermatitis be cured?
- While seborrheic dermatitis cannot be cured, it can be effectively managed with proper skincare, medicated shampoo, and lifestyle modification.



