India’s Economic Growth: A Comprehensive Overview – India, one of the fastest-growing economies in the world, has witnessed remarkable progress in recent decades. This article delves into the various aspects of India’s economic growth journey, analyzing the factors driving it, the challenges it faces, and the policies shaping its trajectory.
Historical Context
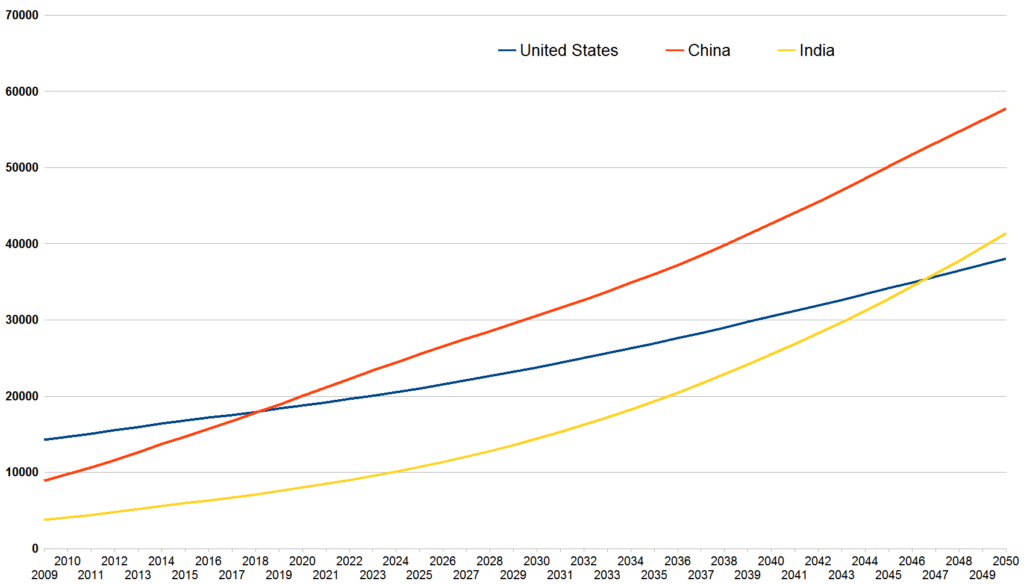
India’s economic history is a tale of resilience and transformation. From the colonial era to independence and beyond, the nation has navigated through phases of stagnation and liberalization. Post-independence, the economy grappled with socialist policies, but the 1991 economic reforms unleashed its potential for growth.
Factors Driving Economic Growth
1. Technology and Innovation
India’s prowess in technology and innovation has been a significant driver of economic growth. The IT and software services industry, in particular, has played a pivotal role in positioning India as a global hub for outsourcing and technology solutions.
2. Demographic Dividend
With a large and youthful population, India enjoys a demographic dividend, providing a substantial workforce and consumer base. However, harnessing this demographic advantage requires investments in education, skill development, and job creation.
3. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Liberalization measures and economic reforms have attracted significant foreign investment into India, fueling growth across sectors such as manufacturing, infrastructure, and services. FDI inflows contribute to technology transfer, employment generation, and export competitiveness.
Challenges and Obstacles
Despite its rapid economic growth, India grapples with several challenges that threaten its sustainability:
1. Income Inequality
Persistent income inequality remains a pressing concern, with disparities evident across regions, sectors, and social groups. Addressing this imbalance is crucial for inclusive growth and social cohesion.
2. Infrastructure Deficits
Inadequate infrastructure, including transportation, energy, and urban amenities, constrains economic productivity and competitiveness. Bridging the infrastructure gap requires concerted investments and policy reforms.
3. Environmental Concerns
Industrialization and urbanization have led to environmental degradation, including pollution, deforestation, and depletion of natural resources. Balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability is imperative for long-term prosperity.
Government Policies and Initiatives
The Indian government has introduced various policies and initiatives to catalyze economic growth:
1. Make in India Campaign
Launched to promote domestic manufacturing and attract foreign investment, the Make in India campaign aims to enhance India’s manufacturing capabilities and create employment opportunities.
2. GST Implementation
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime, implemented in 2017, aims to simplify the tax structure, boost tax compliance, and create a unified national market. Despite initial challenges, GST has streamlined indirect taxation and facilitated ease of doing business.
3. Digital India Initiative
The Digital India initiative seeks to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy. Through investments in digital infrastructure, e-governance, and digital literacy, the program aims to bridge the digital divide and foster inclusive growth.
Sectoral Analysis
India’s economy comprises three primary sectors:
1. Agriculture
Despite its declining contribution to GDP, agriculture remains a vital sector for livelihoods and food security. Enhancing agricultural productivity, promoting sustainable practices, and improving market linkages are essential for rural development.
2. Manufacturing
The manufacturing sector holds immense potential for job creation and export growth. Initiatives such as Make in India and measures to enhance ease of doing business aim to revitalize the manufacturing ecosystem and bolster industrial growth.
3. Service Sector
The service sector, encompassing IT, banking, healthcare, and tourism, constitutes a significant share of India’s GDP. Leveraging India’s strengths in services and fostering innovation can further propel growth and global competitiveness.
Regional Disparities
India’s economic landscape is characterized by stark regional disparities:
1. Urban-Rural Divide
Urban areas exhibit higher levels of economic development, infrastructure, and opportunities compared to rural counterparts. Bridging the urban-rural gap requires targeted investments in rural infrastructure, agriculture, and social welfare programs.
2. Regional Imbalances
Economic disparities persist among states and regions, with southern and western states outpacing their northern and eastern counterparts. Promoting balanced regional development through decentralization and inclusive policies is crucial for equitable growth.
International Trade
India’s engagement in international trade is integral to its economic growth strategy:
1. Bilateral Trade Agreements
India has entered into various bilateral and multilateral trade agreements to enhance market access and promote exports. Strengthening trade ties with key partners fosters economic integration and diversification.
2. Export-Oriented Growth
Export-led growth remains a strategic priority for India, with a focus on sectors such as IT services, pharmaceuticals, and engineering goods. Expanding export markets and improving trade infrastructure are essential for sustaining export competitiveness.
Impact on Society
India’s economic growth has profound implications for society:
1. Poverty Alleviation
Economic growth has lifted millions out of poverty, but poverty remains a pervasive challenge, especially in rural and marginalized communities. Targeted poverty alleviation programs and inclusive development strategies are essential for reducing poverty incidence.
2. Employment Generation
Economic growth generates employment opportunities across sectors, contributing to livelihoods and social mobility. However, the quality of employment, wage levels, and skill mismatches are critical concerns that need to be addressed for inclusive growth.
3. Social Welfare Programs
Government-led social welfare programs, such as the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) and the National Health Mission (NHM), play a crucial role in providing social protection and enhancing human development outcomes.
Future Prospects
Despite challenges, India’s economic outlook remains promising:
1. Projections and Forecasts
Economists project India to sustain robust economic growth in the coming years, driven by structural reforms, demographic dividends, and technological advancements. However, policy coherence and implementation will be critical for realizing growth potential.
2. Emerging Opportunities
Emerging sectors such as renewable energy, digital technology, and healthcare present new avenues for growth and innovation. Capitalizing on these opportunities requires investments in research and development, skill enhancement, and regulatory reforms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, India’s economic growth story is a testament to its resilience, ingenuity, and potential. While challenges persist, concerted efforts by policymakers, businesses, and society can unlock India’s full economic potential and pave the way for inclusive and sustainable growth.
FAQs
- What are the key drivers of India’s economic growth?
- Technology and innovation, demographic dividend, and foreign direct investment are primary drivers of India’s economic growth.
- How has government policy influenced India’s economic trajectory?
- Government policies such as Make in India, GST implementation, and Digital India have aimed to catalyze economic growth and enhance competitiveness.
- What are the major challenges hindering India’s economic development?
- Income inequality, infrastructure deficits, and environmental concerns pose significant challenges to India’s economic development.
- What role does international trade play in India’s economy?
- International trade is integral to India’s economic growth strategy, facilitating market access, export diversification, and economic integration.
- What are the future prospects for India’s economy?
- Despite challenges, India’s economic outlook remains promising, with opportunities for growth in emerging sectors and sustained reforms.



